6 Bedroom House Design Planning & Style
Design Considerations for a 6-Bedroom House
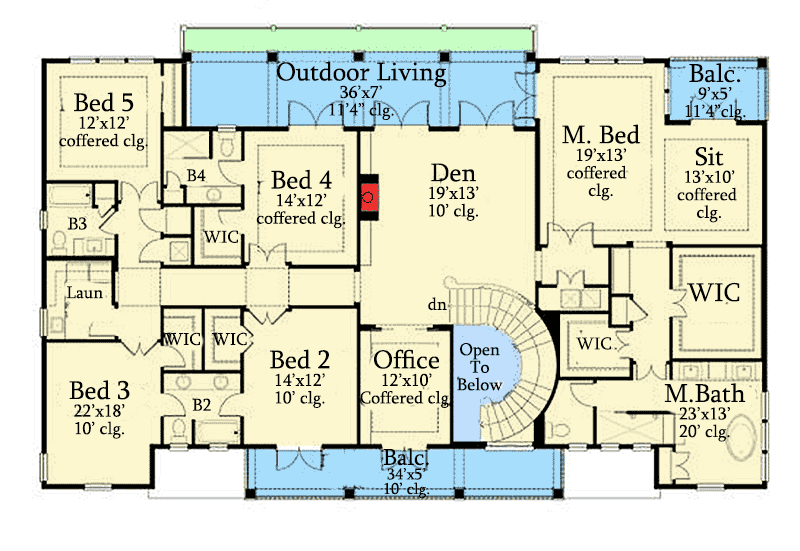
6 bedroom house design – Designing a six-bedroom house requires careful consideration of family dynamics, lifestyle, and future needs. The layout should prioritize functionality and flow, ensuring a comfortable and efficient living space for all occupants. Material selection plays a crucial role in both aesthetics and long-term cost-effectiveness.
Ideal Layout for a Six-Bedroom House
A successful six-bedroom house layout often incorporates zones for different family members or functions. A master suite with a large ensuite bathroom and walk-in closet is typically situated for privacy. Children’s bedrooms could be grouped together near a shared bathroom, fostering a sense of community. Additional bedrooms might serve as guest rooms, home offices, or hobby spaces.
Designing a six-bedroom house presents unique spatial challenges, requiring careful consideration of flow and functionality. However, even with such a large scale, understanding efficient space planning is crucial, much like the principles applied in a smaller project, such as design for two bedroom house. Applying similar concepts of maximizing natural light and creating distinct zones helps ensure a comfortable and well-utilized six-bedroom home, regardless of its size.
Consideration should be given to the location of shared living areas, such as the kitchen, dining room, and family room, to ensure easy access and flow between these central spaces and the bedrooms. Placement of laundry facilities, storage areas, and other essential rooms is also vital for seamless daily living. For instance, a family with older children might prefer bedrooms on separate wings, whereas a family with young children may prefer bedrooms clustered together.
Architectural Styles Suitable for a Six-Bedroom House, 6 bedroom house design
Several architectural styles lend themselves well to the scale and complexity of a six-bedroom home. A sprawling Ranch style, characterized by its single-story design and long, low profile, offers ease of access and practicality, particularly for families with young children or elderly members. Conversely, a two-story Colonial style, with its symmetrical façade and formal elegance, provides a more traditional and stately aesthetic.
Modern Farmhouse styles, blending rustic charm with contemporary design elements, are popular for their versatility and appeal. Finally, Mediterranean Revival homes, with their stucco exteriors, arched doorways, and terracotta roofs, offer a unique and visually striking design, particularly in warmer climates. The choice depends on personal preference, the surrounding environment, and the overall desired aesthetic. For example, a Ranch style might be best suited for a large, flat lot, while a Colonial style might be more appropriate for a smaller, more established neighborhood.
Building Material Selection for a Large Residence
Choosing building materials for a large residence is a significant decision impacting cost, durability, maintenance, and aesthetic appeal. Factors to consider include climate, budget, and personal preferences. The following table compares four common exterior wall materials:
| Material | Cost (Relative) | Durability | Maintenance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brick | High | Very High | Low |
| Wood Siding | Medium | Medium | Medium-High |
| Vinyl Siding | Low | Medium-High | Low |
| Stucco | Medium | High | Medium |
Note: Cost is relative and varies depending on location, quality, and labor costs. Durability and maintenance requirements also depend on factors such as climate and proper installation. For example, wood siding requires regular painting or staining to prevent rot and insect damage, while brick requires minimal maintenance. Vinyl siding offers a low-maintenance option with good durability, while stucco provides a durable, aesthetically pleasing finish but may require occasional repairs.
Sustainability and Energy Efficiency: 6 Bedroom House Design
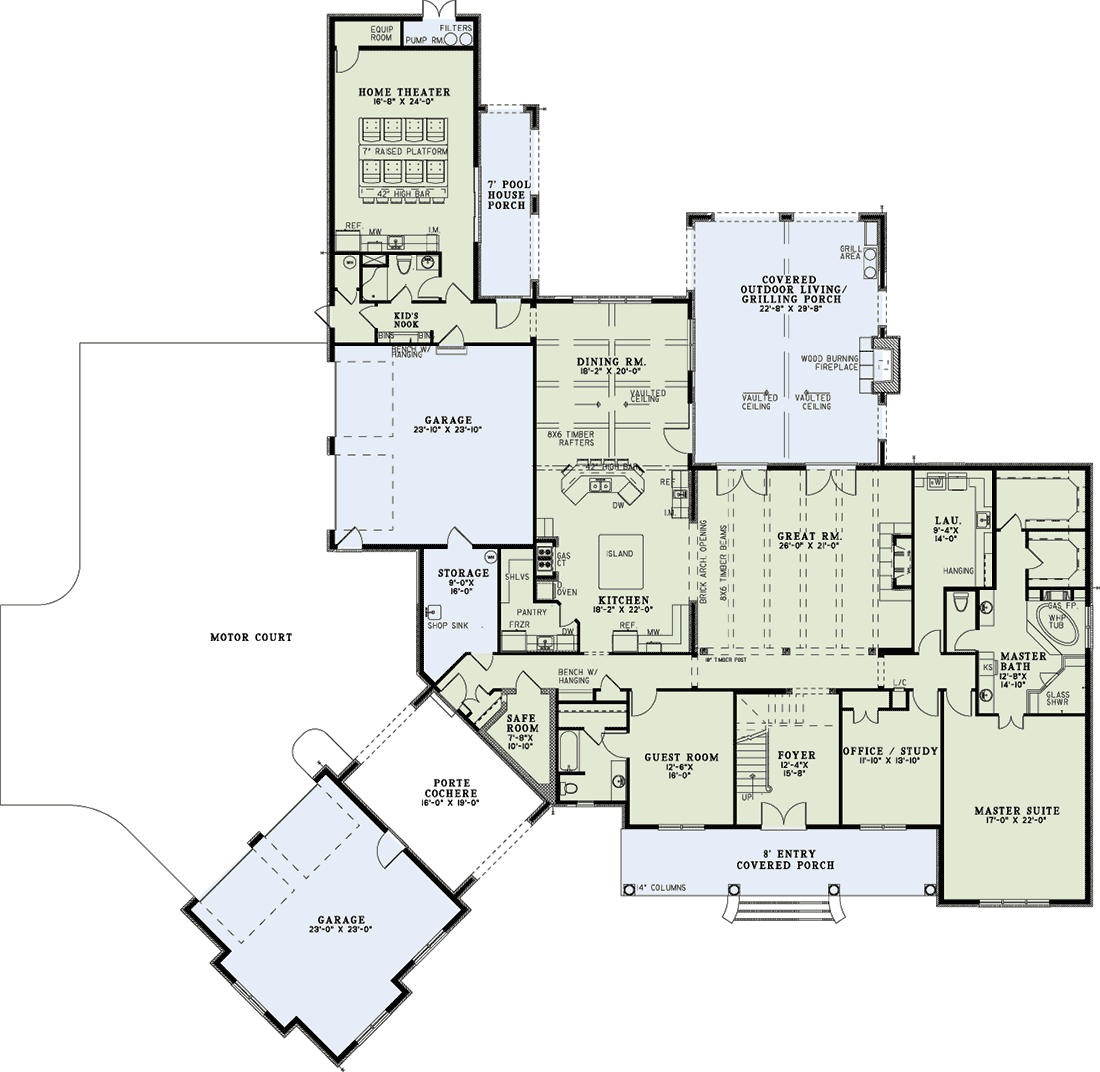
Designing a six-bedroom house presents a unique opportunity to prioritize sustainability and energy efficiency. While larger homes inherently consume more resources, thoughtful planning and the incorporation of eco-friendly materials and technologies can significantly reduce the environmental impact and operating costs. This section details strategies for creating a sustainable and energy-efficient six-bedroom home.Sustainable building materials and practices are crucial for minimizing the environmental footprint of a large home.
The selection of materials with low embodied carbon, recycled content, and responsible sourcing is paramount. This includes considering options like sustainably harvested lumber, recycled steel, and low-VOC paints. Furthermore, efficient construction techniques that minimize waste and maximize resource utilization should be employed. For instance, prefabrication can reduce on-site waste and construction time, while careful planning can optimize material usage.
Sustainable Building Materials
The use of sustainable materials directly impacts the environmental impact of the building throughout its lifespan. Examples of sustainable materials include reclaimed wood, bamboo, recycled concrete, and locally sourced stone. Reclaimed wood, for example, reduces deforestation and offers unique aesthetic qualities. Bamboo is a rapidly renewable resource with high strength-to-weight ratio, suitable for flooring or structural elements. Recycled concrete reduces the demand for virgin materials and minimizes landfill waste.
Locally sourced materials reduce transportation emissions, lowering the overall carbon footprint. The choice of sustainable materials should consider factors such as durability, maintenance requirements, and lifecycle cost.
Maximizing Energy Efficiency
A large home like a six-bedroom residence requires careful consideration of energy efficiency to minimize operational costs and environmental impact. Effective insulation is critical in reducing heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer. High-performance insulation materials, such as spray foam insulation or dense-packed cellulose, can significantly improve the home’s thermal performance. Strategic placement of insulation in walls, roofs, and floors minimizes energy transfer, resulting in lower heating and cooling demands.
Proper sealing of air leaks around windows, doors, and other penetrations is equally important to prevent drafts and energy loss.
High-Performance Windows
Window selection plays a vital role in energy efficiency. High-performance windows with low-E coatings and multiple panes significantly reduce heat transfer. Low-E coatings reflect infrared radiation, minimizing heat gain in summer and heat loss in winter. Multiple panes create an insulating air space that further reduces energy transfer. The orientation and size of windows should also be optimized to maximize natural daylighting and minimize solar heat gain.
South-facing windows, for example, can be strategically sized to maximize passive solar heating in winter, while west-facing windows might benefit from exterior shading to reduce solar heat gain in summer. Proper window installation is also crucial to prevent air leakage.
Renewable Energy Integration
Incorporating renewable energy sources into the design of a six-bedroom house is a significant step towards environmental responsibility and long-term cost savings. Photovoltaic (PV) solar panels can generate electricity to power the home, reducing reliance on the grid. The roof area of a large house provides ample space for solar panel installation. The system’s size should be carefully calculated to meet the home’s energy needs, taking into account factors such as energy consumption patterns, solar irradiance, and shading.
A well-designed solar PV system can significantly reduce or even eliminate electricity bills. Geothermal heating and cooling systems utilize the stable temperature of the earth to provide efficient heating and cooling. These systems can significantly reduce energy consumption compared to traditional HVAC systems. The installation of a geothermal system requires drilling boreholes, but the long-term energy savings and reduced environmental impact often outweigh the initial investment.
Key Questions Answered
What are common challenges in designing a 6-bedroom house?
Common challenges include maximizing natural light in all rooms, efficient space planning to avoid a sprawling layout, managing costs effectively, and ensuring adequate storage solutions.
How can I ensure good airflow and ventilation in a large house?
Proper ventilation can be achieved through strategically placed windows, skylights, and a well-designed HVAC system. Consider cross-ventilation strategies and the use of exhaust fans in kitchens and bathrooms.
What are some cost-effective building materials for a 6-bedroom house?
Cost-effective materials depend on your region and preferences, but exploring options like engineered wood, fiber cement siding, and brick alternatives can offer a balance of affordability and durability.
How can I incorporate smart home technology into a 6-bedroom house?
Smart home technology can enhance security, energy efficiency, and convenience. Consider incorporating smart lighting, thermostats, security systems, and entertainment systems.



