2 Story House Plan Design A Comprehensive Guide
Design Considerations for Different Lot Sizes
2 story house plan design – Lot size significantly influences the design and functionality of a two-story house. A larger lot offers greater flexibility in terms of house size, landscaping, and overall layout, while a smaller lot necessitates a more compact and efficient design to maximize usable space and minimize impact on the surrounding area. Careful consideration of the lot’s dimensions, shape, and orientation is crucial for creating a harmonious and functional home.
Lot Size Impact on Two-Story House Design
The dimensions of the lot directly impact the footprint of the house. Small lots necessitate smaller homes to allow for adequate setbacks and landscaping, whereas larger lots can accommodate more expansive floor plans with features like larger garages, extensive outdoor living spaces, and swimming pools. The shape of the lot also plays a role; irregular lots might require creative solutions to optimize space utilization and minimize wasted areas.
Finally, lot orientation influences the placement of windows and doors to maximize natural light and passive solar gain, impacting both energy efficiency and comfort.
Two-Story House Plans Optimized for Different Lot Sizes, 2 story house plan design
The following examples illustrate how two-story house plans adapt to various lot sizes:
Small Lots (under 5000 sq ft):
- Narrow-lot designs maximize depth while minimizing width, often featuring a long, narrow footprint to fit comfortably within the lot boundaries. These plans typically prioritize efficient space planning with multi-functional rooms and minimal hallways.
- Attached garages are common to save space, often integrated into the house design to create a more cohesive look. Outdoor spaces are typically smaller, focusing on intimate patios or small gardens.
- Emphasis is placed on vertical space utilization, using features like lofts or built-in storage to maximize usable area without increasing the footprint.
Medium Lots (5000-10000 sq ft):
- These lots offer more flexibility, allowing for a wider range of house sizes and layouts. Detached garages are more feasible, offering more storage and separation from the living areas.
- Plans often incorporate larger living areas, more bedrooms, and potentially additional features like a home office or a guest suite. Larger yards allow for more extensive landscaping and outdoor entertainment spaces.
- Design considerations can include a greater emphasis on outdoor living, with features like decks, patios, and gardens integrated into the overall plan.
Large Lots (over 10000 sq ft):
- Large lots permit substantial house sizes, allowing for multiple living areas, expansive bedrooms, and extensive storage. Large detached garages, often with workshops or additional storage space, are common.
- Extensive landscaping is a key feature, with options for large gardens, pools, and extensive outdoor entertainment areas. House placement can be strategically planned to maximize views and privacy.
- Architectural styles can be more elaborate and varied, offering greater design freedom and the possibility of incorporating unique features.
Designing for Sloped Lots
Designing a two-story house on a sloped lot presents unique challenges, requiring careful consideration of site grading, foundation design, and access.
Designing a two-story house plan requires careful consideration of space and flow. The optimal design often depends on cultural preferences, prompting the question: what country have the best house design ? Understanding different architectural styles informs choices like room placement and overall aesthetic, ultimately influencing the success of your two-story home plan.
Challenges and Solutions:
- Foundation Costs: Sloped lots often require more complex and expensive foundations, such as retaining walls or tiered foundations, to ensure stability and prevent soil erosion. Solutions include careful site analysis to determine the most cost-effective foundation type and exploring options like walkout basements to maximize usable space.
- Accessibility: Access to the house and different levels can be challenging on a sloped lot. Solutions involve careful planning of walkways, driveways, and stairs to ensure safe and convenient access. Elevators or ramps may be considered for accessibility.
- Landscaping: Maintaining and landscaping a sloped lot requires careful planning to prevent erosion and create visually appealing outdoor spaces. Solutions include retaining walls, terraced landscaping, and the use of native plants adapted to the slope.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability in Design
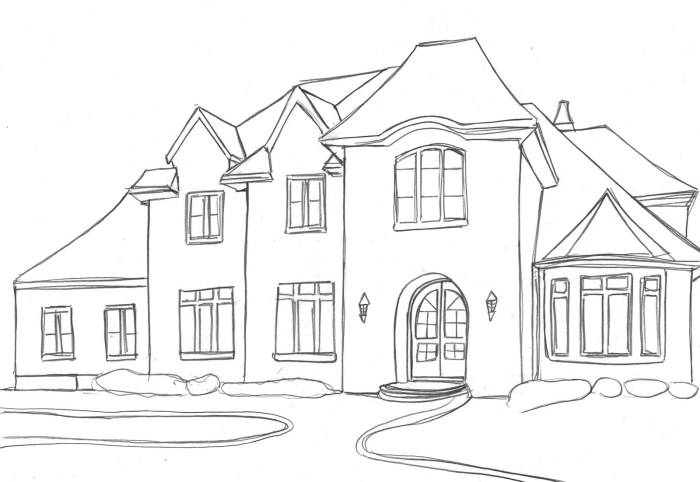

Designing a two-story home with energy efficiency and sustainability in mind not only reduces environmental impact but also translates to significant long-term cost savings for homeowners. By thoughtfully integrating various strategies throughout the design process, we can create homes that are both comfortable and environmentally responsible. This involves careful consideration of building materials, energy systems, and overall building orientation.Incorporating energy-efficient features and sustainable building materials into a two-story house plan offers a multitude of benefits.
These range from lower utility bills and a smaller carbon footprint to improved indoor air quality and enhanced property value. The initial investment in sustainable practices often pays for itself over the lifespan of the home, contributing to a more resilient and environmentally conscious living space.
Energy-Efficient Design Strategies
Several design strategies can significantly improve a two-story home’s energy efficiency. Proper building orientation, maximizing natural light and ventilation, and minimizing heat gain and loss are crucial. For instance, positioning the home to take advantage of prevailing winds can naturally cool the house, reducing reliance on air conditioning. Similarly, strategic placement of windows can optimize solar heat gain in winter and minimize it in summer.
Insulation, both in walls and roofs, plays a vital role in reducing energy consumption for heating and cooling. High-performance windows and doors are essential for minimizing air leakage and maintaining consistent indoor temperatures. Finally, the incorporation of passive solar design elements, such as overhangs to shade windows in summer, can further enhance energy efficiency.
Sustainable Building Materials
The use of sustainable building materials significantly reduces the environmental impact of construction and improves the overall sustainability of the home. Examples include reclaimed wood, bamboo, recycled steel, and locally sourced materials, minimizing transportation emissions. These materials often possess superior durability and longevity compared to conventional options, reducing the need for replacements over time. The embodied energy—the energy consumed in the manufacturing, transportation, and installation of materials—is significantly lower for sustainable options, contributing to a smaller overall carbon footprint.
For example, using sustainably harvested lumber reduces deforestation and supports responsible forestry practices.
Window Types and Energy Efficiency
Different window types significantly impact a two-story home’s energy efficiency. High-performance windows, featuring multiple panes of glass with low-E coatings and argon gas fills, offer superior insulation compared to single-pane windows. These coatings reflect infrared radiation, minimizing heat transfer. The use of argon gas further improves insulation by reducing conductive heat transfer. Triple-pane windows offer even better insulation but come with a higher initial cost.
The impact on heating and cooling costs is substantial; high-performance windows can significantly reduce energy consumption compared to standard windows, leading to lower utility bills and a smaller carbon footprint. For instance, a study by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory showed that high-performance windows can reduce heating and cooling costs by up to 30% compared to standard windows.
Expert Answers: 2 Story House Plan Design
What are the typical costs associated with building a two-story house?
Building costs vary significantly based on location, materials, finishes, and the overall size and complexity of the design. It’s best to consult with local builders for accurate estimates.
How long does it typically take to build a two-story house?
Construction timeframes depend on factors like weather conditions, material availability, and the complexity of the design. A typical timeline ranges from 6 to 12 months, but this can vary considerably.
What are some common zoning regulations to consider?
Zoning regulations vary by location and often dictate setbacks, building height restrictions, and allowable square footage. Check with your local planning department for specific requirements.
What are the best ways to ensure good natural light in a two-story home?
Strategic window placement, skylights, and light wells can maximize natural light penetration. Consider using large windows on the south side (in the northern hemisphere) to take advantage of solar gain.

